| Risk management responsibilities are manifold. In a company, there are many more than just four. This is obvious since everyone is responsible for their own work at the subsidiary level. But if I were to list four responsibilities as assignments in risk management that are very important, which would they be? | In this post I give my own opinion, not that of any organization. |
What are the four responsibilities in risk management and why them?
Ideally, the four responsibilities should be chosen in such a way that they can be based on normal rules of life.
The four most important responsibilities to work out are those on which you can further develop the entire risk management:
- Risk process
- Risk awareness
- Risk Leadership
- Risk Management Audit
Contents
In the margins: what do you base these responsibilities on?
The four commandments of risk management on which these responsibilities can be based are:
- Avoid hurting yourself. Or have a healing effect.
- Avoid hurting others. Or help them.
- Prevent senseless destruction and loss. Or work creatively.
- Seize your opportunities.
How an organization does this is decided by the Chief Resilience Officer. It depends on the culture or cultures of the organization. I will now give a brief description of each of my chosen assignments/responsibilities.
Risk process: What are the steps?
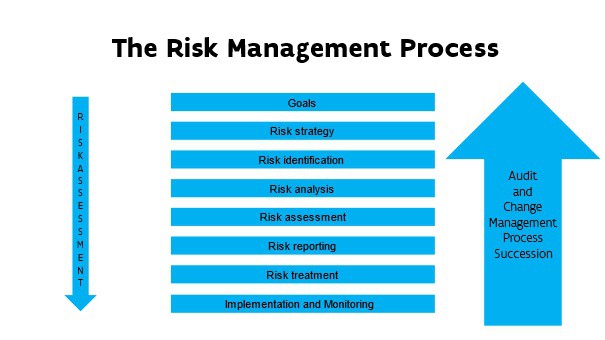
The risk management process consists of a systematic and regular investigation of all possible risks
- that threaten the people and the tangible and intangible interests and activities of the organization and linked to this, a concrete approach to prevent these threats in whole or in part, to continue to guarantee the organization’s objectives.
- that provide opportunities for the organization and linked to this, a concrete approach to maximize or optimally utilize the associated benefits to exceed the organization objectives.
Risk awareness: Especially: what is risk perception?
The extent to which something is perceived as a risk and how large this risk is estimated.
This depends on the intuitive assessment.
Even if the risk can be calculated and assessed as ‘low’ on that basis, this says little about how the risk is perceived.
It includes the assessment of the risk from everyday perception and decision-making. An identical risk can be perceived and assessed differently by different people.
The same person may assess an identical risk differently at a different time and place. So, it’s subjective. It is influenced by a range of factors.
- Voluntary or forced?
- Control or lack of control?
- Fair distribution of the risk?
- Exceptional risk?
- Chance of something horrifying?
- Natural or artificial risk?
- Familiar with the risk?
- Chance that something will happen to children?
- Is one personally affected?
Risk Management Audit
A risk management audit is a process of assessing and evaluating the effectiveness of risk management policies and practices within an organization. The main purpose of such an audit is to verify the organization’s ability to adequately identify, assess, treat, and monitor its risks. Some key aspects of a risk management audit include:
- evaluation of risk management processes;
- compliance with laws and regulations;
- assessment of risks and vulnerabilities;
- assessment of risk management measures;
- monitoring and reporting;
- recommendations and improvements.
The goal is to ensure that the organization is well prepared for potential risks and can manage them effectively. This contributes to the sustainable growth and continuity of the organization.
Risk Leadership: What is Risk Leadership?
The statement is: “Everyone is a risk leader!” (Martin Van Staveren)
| The risk manager (RM: risk management) | The Risk Leader (RL: Risk Leadership) |
| Practices Risk Management | Risk-based |
| Focuses on risk | Has goals as a focus |
| Objectifies and quantifies | Subjectivates and qualifies |
| Manages risks | Deals with risks |
| Leverage models | Leverage processes |
| Is a staff position | Is a role model |

